Abstract
- Stands for Portable Operating System Interface
- A set of standards designed by IEEE for Library Call, specifying the interface between Kernel and OS System Program. Comes with a set of automated conformance test to check if a kernel is POSIX-compatible
- Has about 100 Library Call, but not one-to-one mapped to System Call (系统调用). Below is a list of major POSIX system calls
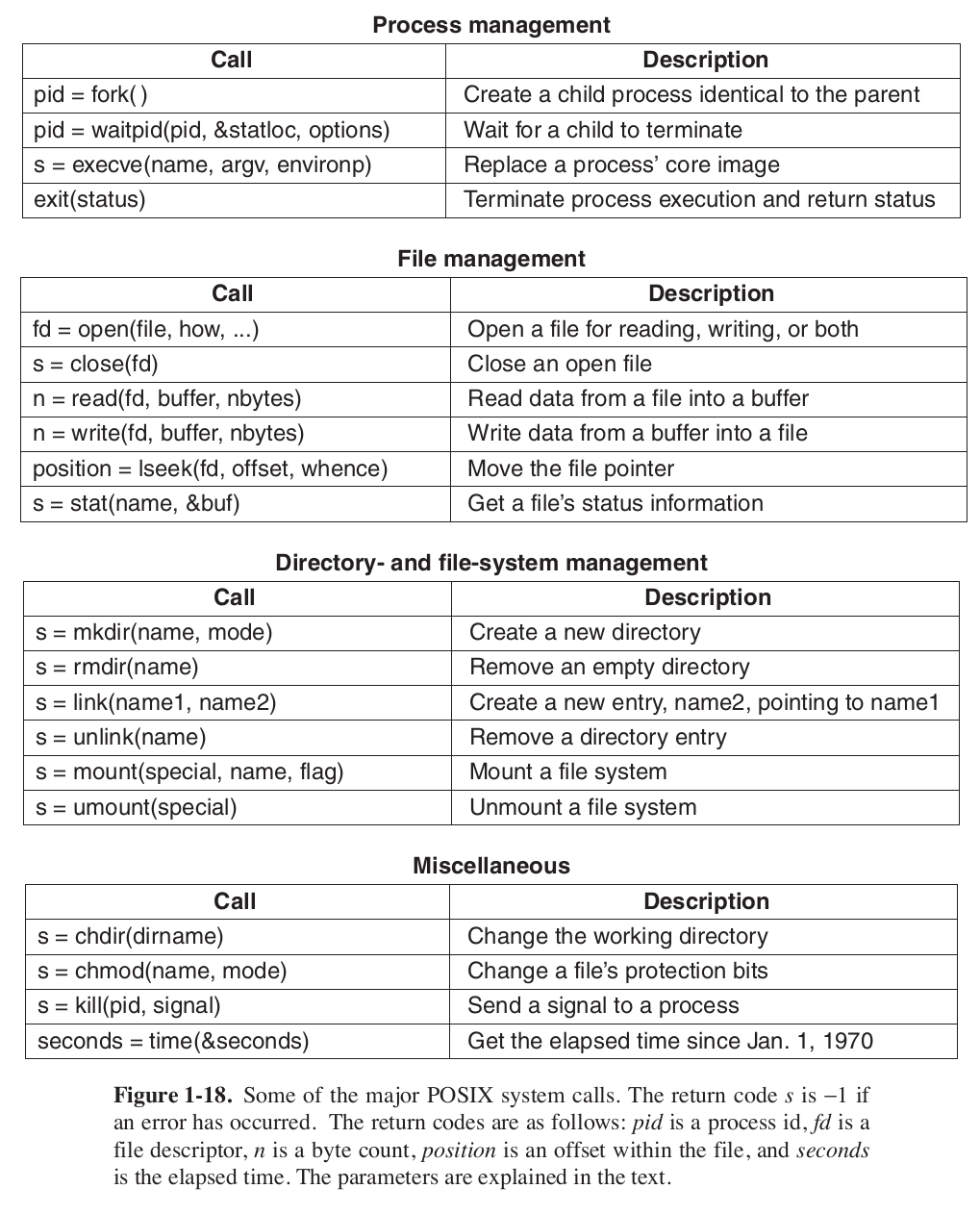
Important
For Linux, it is the combination of Linux Kernel and libc that provides the POSIX API.
libcadds a decent amount of value - not every POSIX function is necessarily a system call, and for the ones that are, the kernel behaviour isn’t always POSIX conforming.So decoupling out some of the POSIX implementations into
libc, we achieve a faster and more POSIX-compliant system. It is faster because we reduce the involvement of kernel, involving kernel is expensive! Great overhead introduced by Trap Interrupt (陷入) and Interrupt Handler etc.
Write Once, Run (Mostly) Anywhere
POSIX ensures compatibility and portability of applications across different Unix-like operating systems.
A POSIX-compliant application written using the standard system calls should be compatible across different POSIX-compliant operating systems. This massively reduces the development effort for cross-platform software.
Guidance for kernel vendores
Kernel vendors have a blueprint for the set of system calls that should ideally be implemented in their systems for better standardisation.
