Abstract
- An Unix-like Socket that provides Inter-Process Communication (IPC) using File Descriptor, where the Kernel handles the System Call (系统调用) and put the mechanism behind a Abstraction Barrier
Unix Domain Socket Lifecycle
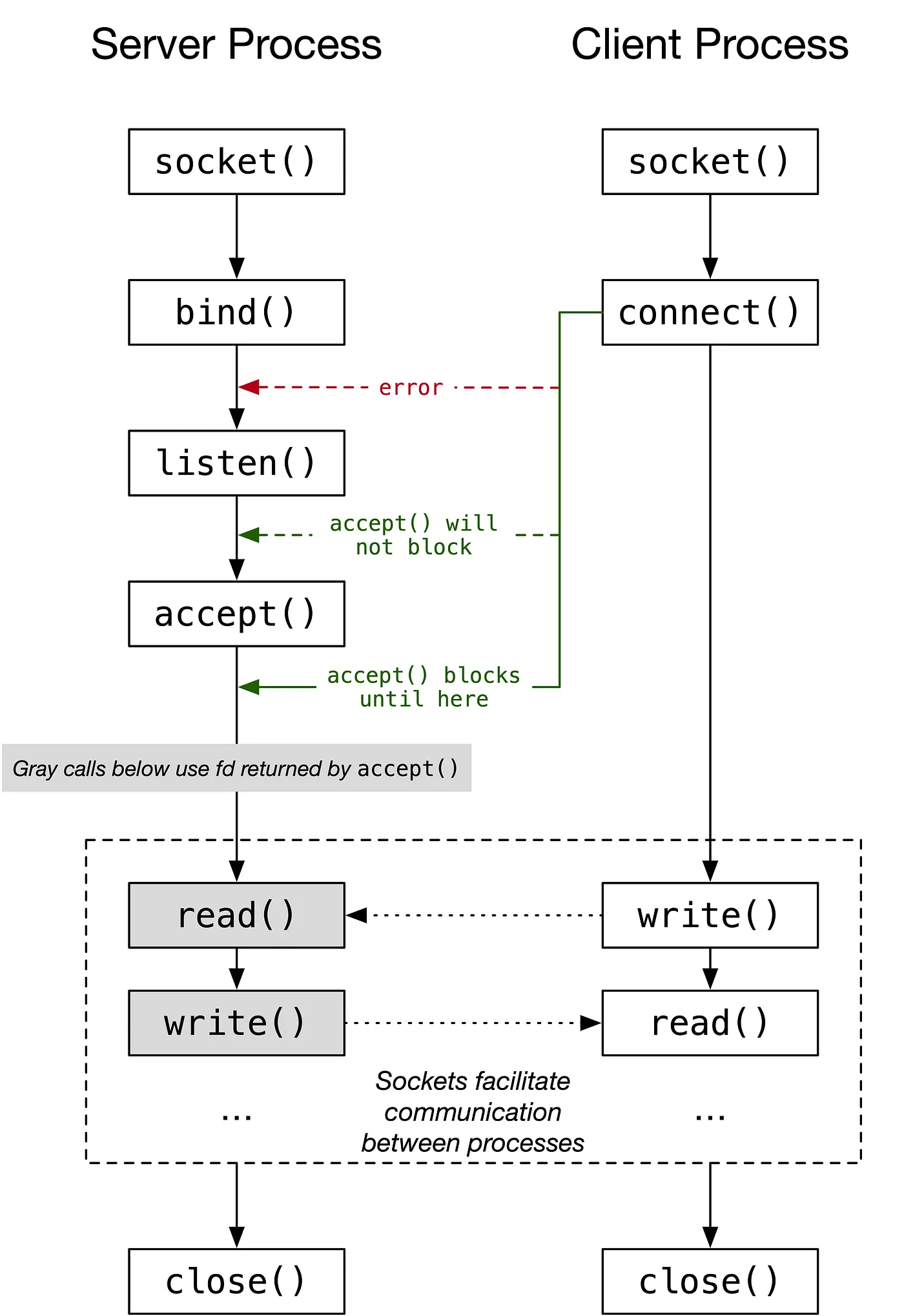
- The above diagram show the System Call (系统调用) used to implement Unix Domain Socket
Server Process
socket()- creates a new Unix Domain Socket & returns a File Descriptor that can be used to refer to the socket in future system callsbind()- bind the socket to a Pathname, so that the client can connect to itlisten()- mark the socket as passive, so the socket that will accept incoming connection requestsaccept()- accept an incoming connection. This call blocks until a connection request arrives. Note that this function will error out iflisten()is not called beforehand. Importantly, this call creates a new socket that is connected to the peer socket(peer socket = the socket at the other end of the connection, in this case, socket created by client process) and returns a file descriptor associated with it. So, if you want to communicate with the peer socket, you should use the file descriptor returned fromaccept(), not the file descriptor returned from the call tosocket(). The latter socket remains open and is used to accept further connection requests
Client Process
socket()- creates a new Unix Domain Socket & returns a File Descriptor that can be used to refer to the socket in future system calls. Note that by default, a socket created usingsocket()is marked as active, and can be used in aconnect()call to connect to a passive socketconnect()- connects to a passive socket on the pathname specified when the server performs thebind(). Note thatconnect()should be called afterlisten()is called on the server socket, otherwise it will error. However, it can be called beforeaccept()
Communication takes place
read()write()
End
close()
Note
Server socket can accept many client connections at the same time.
Code Example
You can refer to this Medium Article that implements UNIX Domain Socket on both the client and server using C.
